Join a powerful, unprecedented alliance for better eye health for all.
Join IAPBFormulating the goals is a key step in the development of a programme. A goal is the positive change that would come about as a result of successful implementation of the programme. It represents the ultimate outcome that we want to achieve. Multiple goals can be formulated to cover different parts of the programmes. Once the goals have been established, the inputs and activities required to reach these goals need to be determined. A theory of change or logic model can help in visualising the steps leading to the desired outcomes.

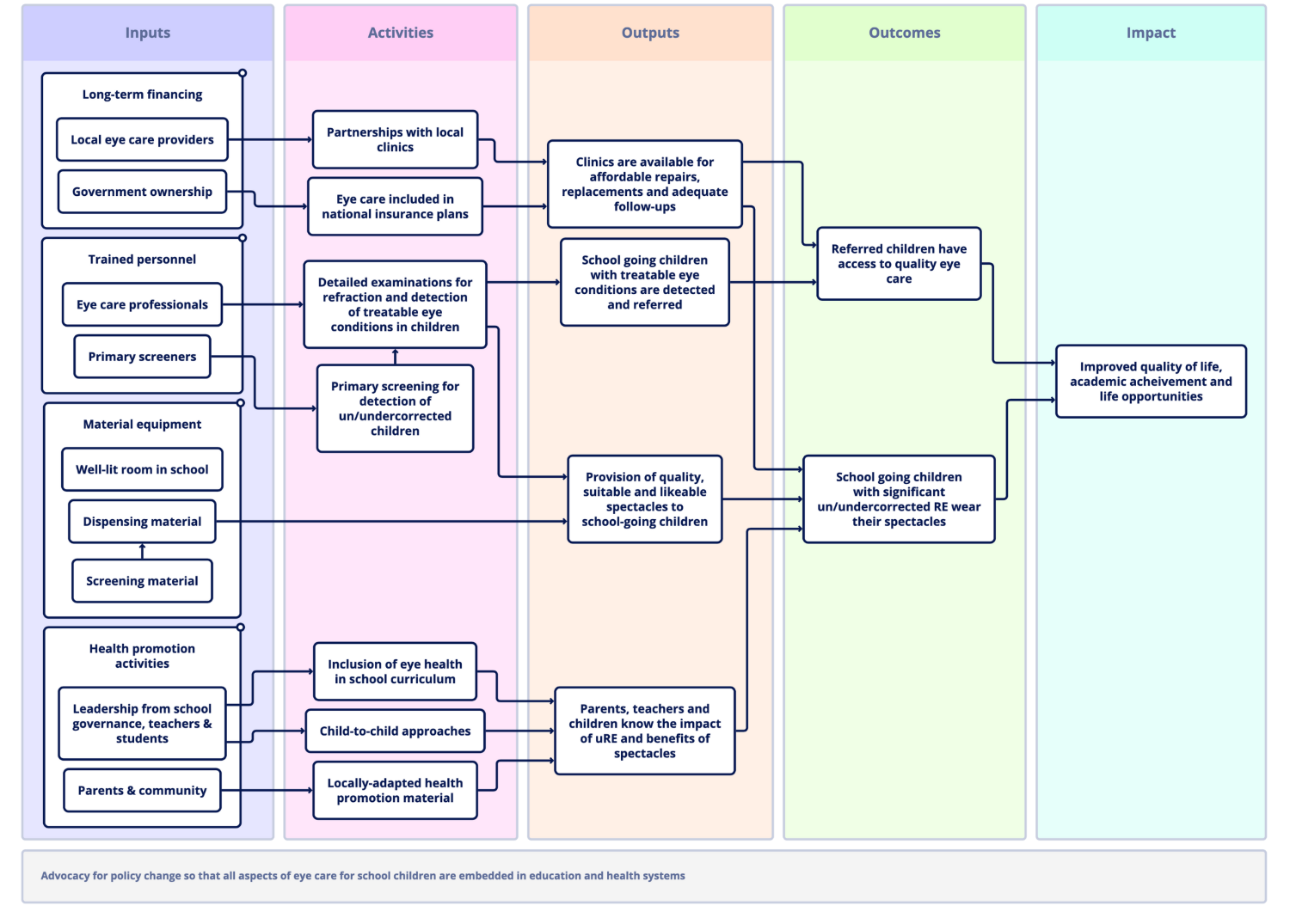
For each outcome, a SMART objective must be formulated: Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant and Time-based. For example:
Assessing the gaps between the current situation and the ‘ideal’ situation can help formulate the objectives.
Potential barriers to the programme should also be considered and assessed when planning the programme.
Qualitative research such as focus groups or key informant interviews can be useful to identify local barriers if a lack of information or local contextual understanding exists.
Example: Girls do not like wearing glasses. School nurses are overloaded.
| Desired outcome | Current situation | Objective | Potential barrier | Possible solutions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| All children wear their spectacles | Only 30% of children wear their spectacles | Obtain 70% spectacle wear rate at 6-month follow-up | Girls don’t wear their spectacles because they are teased | – Let the young girls choose their frames with a friend
– Targeted education campaign in schools |